AC Joint Injury
What is an AC Joint Injury?
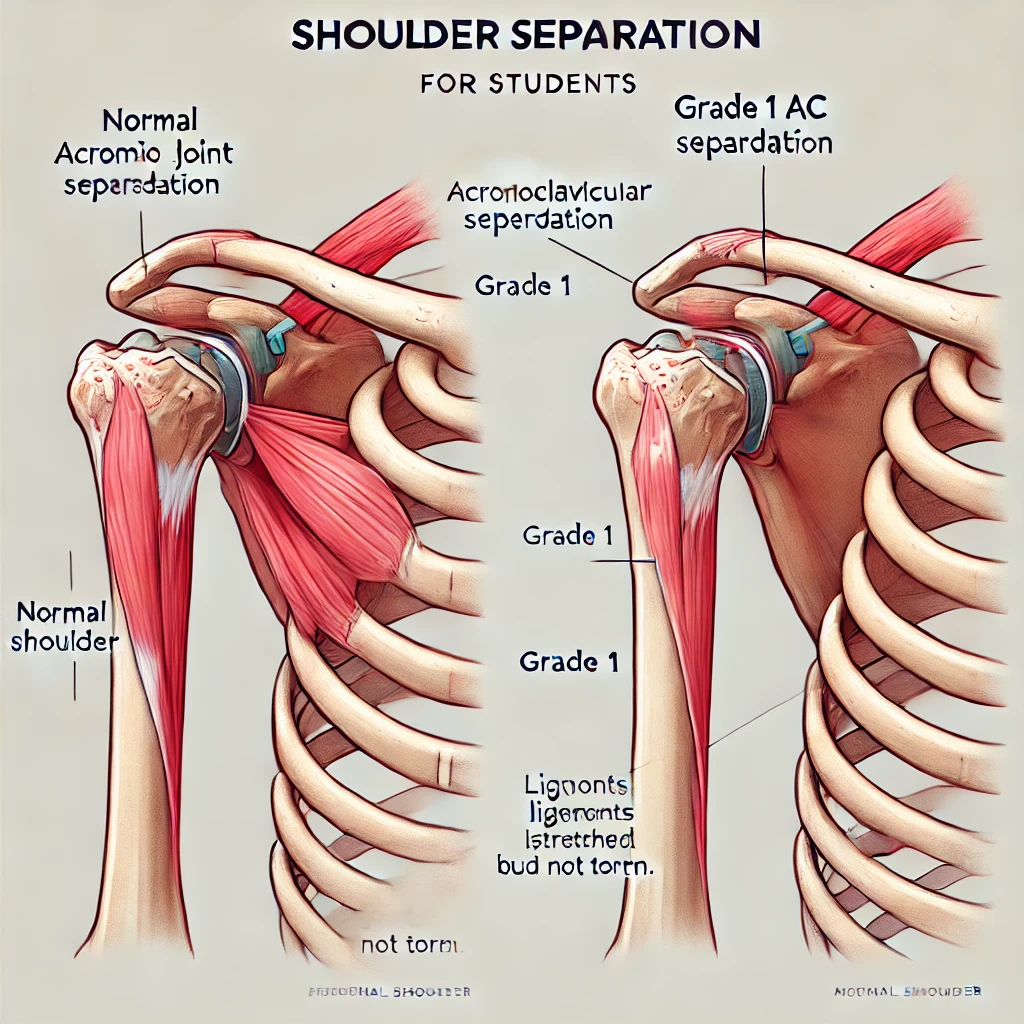
The shoulder consists of three joints: the glenohumeral joint, the acromioclavicular (AC) joint, and the sternoclavicular joint. A shoulder separation typically refers to an injury at the AC joint, where the highest point of the shoulder (acromion) and the collarbone (clavicle) meet.
During a shoulder separation, the ligaments connecting these bones can be stretched or torn, causing the acromion to move away from the clavicle. This injury often occurs due to direct trauma, such as falling on the shoulder or experiencing a high-impact collision during sports like football or cycling.
Shoulder Separation vs. Shoulder Dislocation
A shoulder separation is different from a shoulder dislocation. A separation affects the AC joint, whereas a dislocation occurs when the arm bone (humerus) is displaced from the shoulder socket (glenoid). Dislocations may require medical intervention to reposition the joint and are often accompanied by torn ligaments and cartilage damage.
AC Joint Injury Classification
AC joint injuries are classified based on severity:
- Grade 1: Mild pain, no deformity, ligaments remain intact.
- Grade 2: Partial tearing of AC ligaments, slight misalignment.
- Grade 3: Complete ligament tears, significant joint displacement.
- Grades 4-6: Severe ligament disruption requiring surgical evaluation.
Symptoms of a Separated Shoulder
- Intense pain at the time of injury
- Swelling and bruising
- Weakness in the shoulder
- Visible deformity at the top of the shoulder
Diagnosis of AC Joint Injury
A physical examination assesses pain, weakness, and deformity. X-rays may be used to determine injury severity and guide treatment planning.
Treatment Options
Non-surgical Treatment:
Lower-grade injuries are treated with immobilization, rest, ice, and pain management. Recovery may take 1-6 weeks, though some pain may persist for months.
Surgical Treatment:
Higher-grade injuries may require AC joint reconstruction surgery. This minimally invasive procedure stabilizes the joint by repairing torn ligaments, sometimes using a graft. A physical therapy program follows surgery to restore full function.


